
Images of the snake show it is small enough to curl up on a US quarter.
August 3, 2008

Images of the snake show it is small enough to curl up on a US quarter.
I was thrilled when I turned over that rock and found it. After finding the first one, we turned hundreds of other stones to find another one. Biologist Blair Hedges
The world’s smallest snake, averaging merely 4 inches (10 cm) and as thin as a spaghetti noodle, has been discovered on the Caribbean island of Barbados.
The snake, found beneath a rock in a tiny fragment of threatened forest, is thought to be at the very limit of how small a snake can evolve to be.
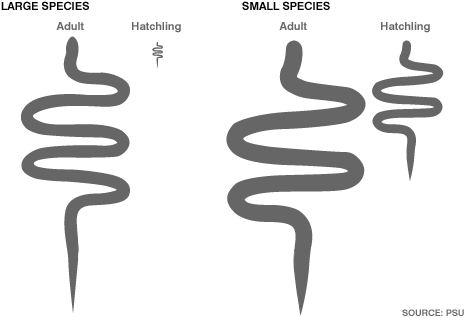
Females produce only a single, massive egg – and the young hatch at half of their adult body weight.
This new discovery is described in the journal of Zootaxa.
The snake – named Leptotyphlops carlae – is the smallest of the 3,100 known snake species and was uncovered by Dr. Blair Hedges, a biologist from Penn State University.
In total, Dr. Hedges and his herpetologist wife found only two females.
Dr. Hedges thinks that the snake eats termites and is endemic to this one Caribbean island. He said that, in fact, three very old specimens of this species were already in collections – one in London’s Natural History Museum and two in a museum in Martinique.
However, these specimens had been misidentified.

The snake’s habitat is usually under rocks eating termites.
Dr. Hedges explained the difficulty in defining a new species when the organism is so small.
Differences in small animals are much more subtle and so are frequently over-looked. The great thing is that DNA is as different between two small snakes as it is between two large snakes, allowing us to see the differences that we can’t see by eye,” ~ Dr. Hedges.
Researchers believe that the snake – a type of thread snake – is so rare that it has survived un-noticed until now.
But with 95% of the island of Barbados now treeless, and the few fragments of forest seriously threatened, this new species of snake might become extinct only months after it was discovered.
In contrast to other species of snake – some of which can lay up to 100 eggs in a single clutch – the world’s smallest snake only produces a single egg.
“This is unusual for snakes but seems to be a feature of small animals,” Dr Hedges told BBC News.
By having a single egg at a time, the snake’s young are one-half the length of the adult. That would be like humans giving birth to a 60-pound (27kg) baby
Dr Hedges added that the snake’s size might limit the size of its clutch.
“If a tiny snake were to have more than one offspring, each egg would have to share the same space occupied by the one egg and so the two hatchlings would be half the normal size.”
The hatchlings might then be too small to find anything small enough to eat.
This has led the researchers to believe that the Barbadian snake is as small as a snake can evolve to be.
The smallest animals have young that are proportionately enormous relative to the size of the adults producing the offspring
As in the case of Leptotyphlops carlae, the hatchlings of the smallest snakes are one-half the length of an adult
The hatchlings of the biggest snakes on the other hand are only one-tenth the length of the adult producing the offspring
Tiny snakes produce only one massive egg – relative to the size of the mother. This is evolution at work, says Dr Hedges
The pressure of natural selection means the size of hatchlings cannot be smaller than a critical limit if they are to survive
BBC’s Science Reporter Jennifer Carpenter’s article, “World’s smallest snake discovered” served as the basis for this report.
About Loren Coleman
Loren Coleman is one of the world’s leading cryptozoologists, some say “the” leading living cryptozoologist. Certainly, he is acknowledged as the current living American researcher and writer who has most popularized cryptozoology in the late 20th and early 21st centuries.
Starting his fieldwork and investigations in 1960, after traveling and trekking extensively in pursuit of cryptozoological mysteries, Coleman began writing to share his experiences in 1969. An honorary member of Ivan T. Sanderson’s Society for the Investigation of the Unexplained in the 1970s, Coleman has been bestowed with similar honorary memberships of the North Idaho College Cryptozoology Club in 1983, and in subsequent years, that of the British Columbia Scientific Cryptozoology Club, CryptoSafari International, and other international organizations. He was also a Life Member and Benefactor of the International Society of Cryptozoology (now-defunct).
Loren Coleman’s daily blog, as a member of the Cryptomundo Team, served as an ongoing avenue of communication for the ever-growing body of cryptozoo news from 2005 through 2013. He returned as an infrequent contributor beginning Halloween week of 2015.
Coleman is the founder in 2003, and current director of the International Cryptozoology Museum in Portland, Maine.
Filed under Breaking News, Cryptotourism, CryptoZoo News, Cryptozoologists, Cryptozoology, New Species